One of the most unusual BSOD errors to appear is the “reference by pointer” BSOD (reference_by_pointer). Trying to track down the cause of this BSOD is tricky, but it usually points to problems that you can easily fix. So, if you’re trying to troubleshoot a reference_by_pointer BSOD error, this guide should help you.
What Causes a Reference By Pointer BSOD Error in Windows 10?
A reference by pointer BSOD error (also known as a reference_by_pointer or 0x00000018 error) usually points to an issue with your system files or device drivers. To help prioritize system resources, Windows internally refers to running elements (such as an open window) as “objects” with numbers that identify how many times the elements are referenced (or used) elsewhere. This value decreases until the object is removed, freeing up your system memory for other running services. When a reference_by_pointer message appears, Windows is seeing an incorrect reference count for a running object. As this could be a serious security issue, Windows will stop and display a BSOD, forcing your system to restart and clearing all active memory in the process. In almost every case, however, this is usually caused by a buggy piece of software. Hardware drivers are the most common cause, with graphics cards and other components like network devices often causing the message. However, it can also be caused by other issues, such as corrupt system files or even failing hardware. Before you try anything else, you should check your BSOD memory dump files for more information. You will find vital clues behind the cause of a reference by pointer BSOD, such as a driver file (with a .sys file extension) or a system process (such as ntosknrl.exe). Once you’ve located a possible cause (such as a malfunctioning driver), you can follow the steps below to resolve the issue.
Switch to Safe Mode for Troubleshooting
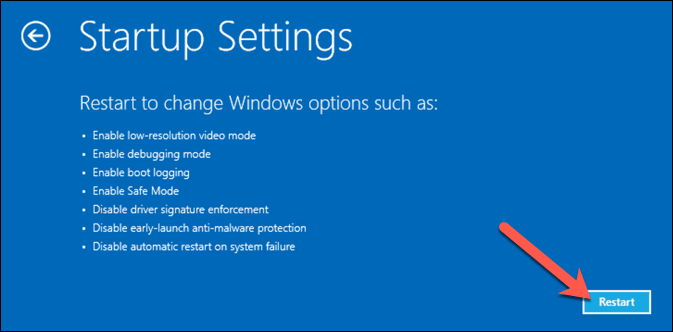
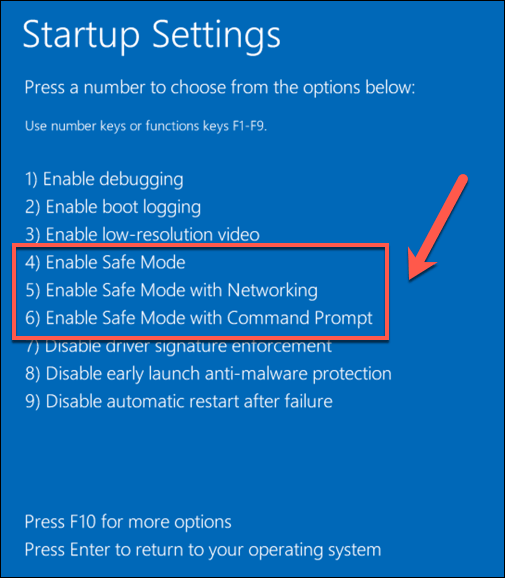
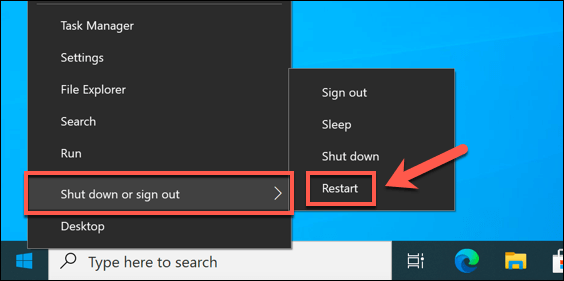
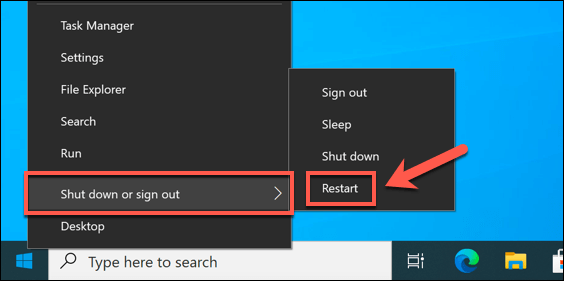
Following a BSOD, your PC is forced to reboot. If stuck in a reference_by_pointer BSOD loop (with each reboot causing another BSOD message), you’ll need to boot into Safe Mode to begin the troubleshooting process. Safe Mode runs Windows with the most basic set of drivers and system processes required to function properly, allowing you to troubleshoot driver issues without risking another BSOD. You can also use Safe Mode to analyze your BSOD dump files before you begin any other attempts to fix the problem. Windows will proceed to boot up using your chosen Safe Mode option, where you can then continue with the troubleshooting steps outlined below.
Update System Files and Device Drivers
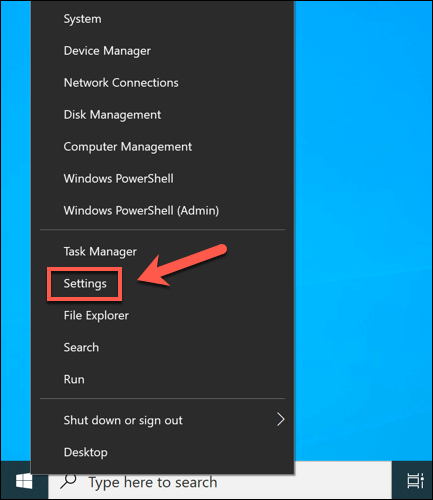
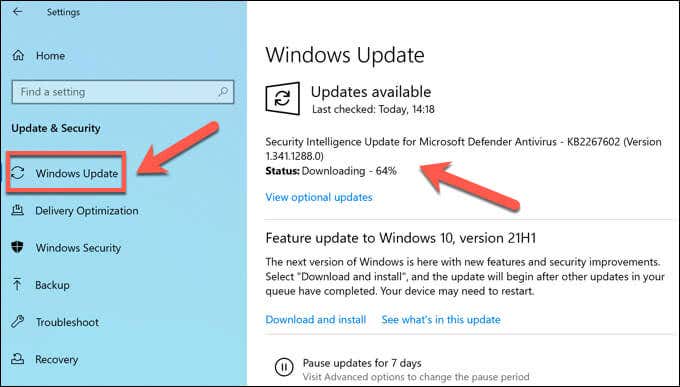
A bug in Windows or a device driver can cause a reference_by_pointer BSOD. To overcome this issue, you’ll need to make sure your system files and drivers are up-to-date using the Windows Update system.
Roll Back a Recently Installed Driver or System Update
While system updates undergo a rigorous testing process, bugs and issues can still occur. If you only see a reference_by_pointer BSOD error after you’ve recently updated your system files or device drivers, you may have introduced a bugged set of files. Thankfully, Windows allows you to roll back a driver on Windows and uninstall any recent Windows updates that are causing issues.
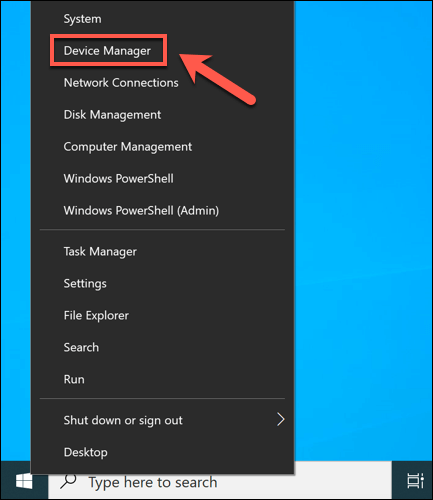
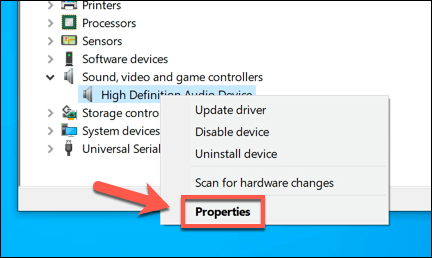
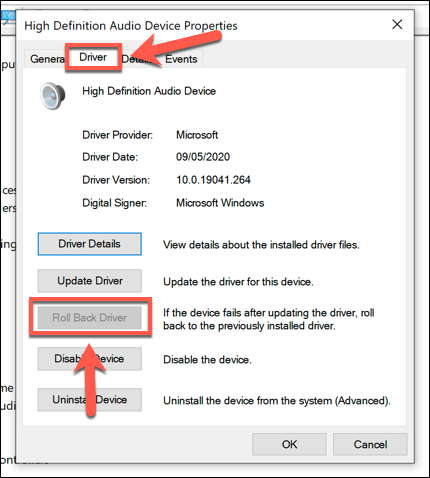
How to Roll Back a Device Driver
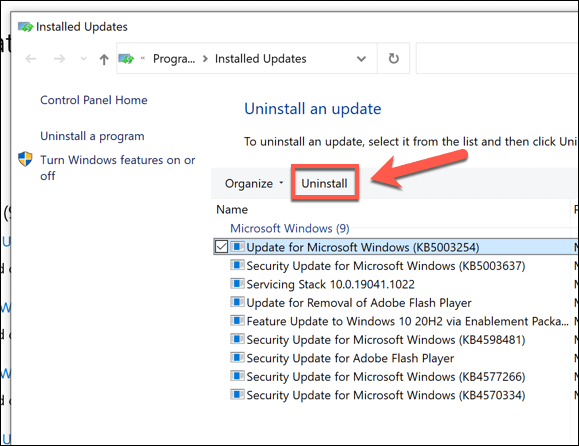
How to Remove a System Update
Check Your System Files for Errors
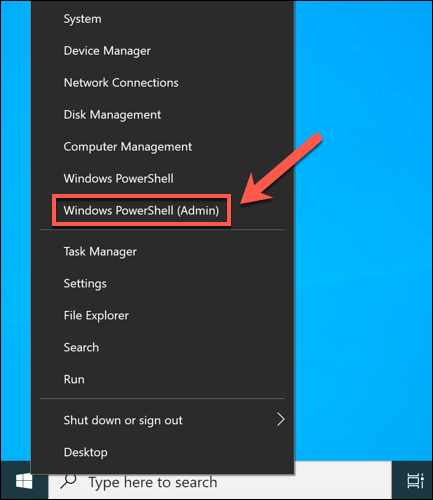
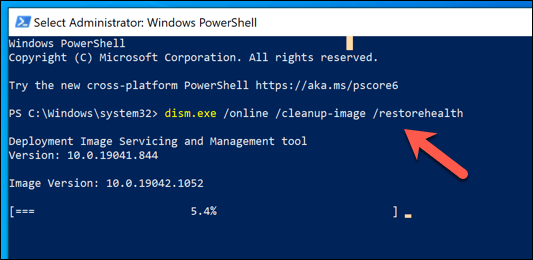
Windows files are constantly changing, with settings and files updated regularly. Unfortunately, your Windows installation will face more catastrophic changes from time to time, from malware infections to hard drive sector failures. If you think that your Windows installation is failing somehow and causing this BSOD error, you can check it for errors using the SFC and DISM tools. Restart your PC once the SFC tool finishes a scan of your Windows installation files. If it can’t update or repair your files, you may need to look at more drastic options, such as resetting Windows 10 with a fresh installation.
Test Your Hardware (and Replace If Required)
Corrupt or buggy files don’t only cause system instability. For example, if your hardware is overheating, overworked, or just plain failing, system errors like a reference by pointer BSOD are the next step before a full PC failure. If heat is an issue, you’ll need to clean out your PC and consider upgrading your cooling to help resolve the issue. Your next step is to test your hardware thoroughly, using CPU stress tests and memory testing tools, as well as checking your hard drive for errors. If your hardware is the problem, your only answer is to replace it. You can replace individual components (such as your motherboard or CPU), but if the PC is too old to repair, you may need to consider a complete upgrade, replacing your PC entirely with a fresh pre-built PC or building your new PC instead.
Recovering from BSOD Errors on Windows
A reference by pointer BSOD error isn’t usually something to worry about, but without regular system maintenance in place, it could point to a serious problem with your PC. Make sure to keep your important files backed up elsewhere so you don’t lose your files when your PC crashes and ensure you have system restore enabled. If you can’t fix the problem using the steps above, you might need to consider more drastic options. If your hardware is faulty, you’ll need to consider upgrading your PC or replacing it entirely. Otherwise, it might be time to wipe and reset Windows to restore stability, although you’ll need to restore your files from a backup afterwards.